8)Calcifying odontogenic cyst(Gorlin cyst).
Calcifying odontogenic cyst is as un common lesion which is widely considered to represent a cyst. Some invetigators classify it as a neoplasm (the solid variant) {Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor} .WHO groups calcifying odontogenic cyst with all its variants (ghost cell tumor, malignant ghost cell carcinoma with cytologic atypia & calcifying odontogenic cyst ) as a neoplasm rather than cyst.
Origin,
Epithelial rests of serres (rests of dental lamina) either in soft tissue or bone.
Clinical features,
-Site of this cyst is predominanrly intraosseous,but 25% occurs occasionally in soft tissue of the gingiva (extra-osseous) or (peripheral).Mostly occurs anterior to first molar in incisors and canine region,it affects mandible and maxilla.
-Below 40 years old.
-Symptomless.
 -Extraosseous or peripheral lesions appear as localized gingival mass resemble fibromas, gingival cysts and peripheral giant cell granulomas.
-Extraosseous or peripheral lesions appear as localized gingival mass resemble fibromas, gingival cysts and peripheral giant cell granulomas. Radiographic picture,
Radiographic picture,Well-defined unilocular radiolucent area or multilocular containing varying amounts of radiopaque calcified materials.



N.B: Some authors say that 30% of gorlin cysts are associated with crown of uneupted teeth, some exhibit that gorlin cyst is of priomordial origin and develops from rests of serres and so it is not associated with crown of impacted tooth and that all gorlin cysts occurs between 2 teeth.
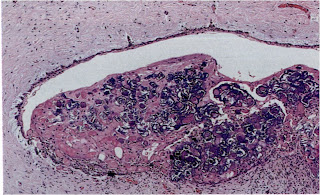
Histopathological features,
-Basal cell layer lining is of cuboidal or columnar cells resembles ameloblasts (ameloblasts-like), the overlyning layer of loosly arranged stellate reticulum -like cells.
-The most characteristic hidtopathological feature of calcifing odontogenic cyst is the presence of Ghost cells, which are eosinophilic altered epithelial cells characterize by loss of nuclei with preservation of cell outline.

-These ghost cells undergo keratinization and calcification, they appear first as basophilic granules (keratinized ghost cells) then it may increase in size to form calcified materials (calcified ghost cells), these calcified ghost cells is the feature which is responsible for radiopacities in the radiographic picture.
-In some cases epithelial lining ,ghost cells, proliferate into lumen so that the lumen is largely filled with masses of calcified ghost cells and the lesion becomes solid (solid ghost cell tumor variant), and as a result of contact between ghost cells and connective tissue ,a foregin body reaction may be elicited due to their exudation of keratin so multinucleated giant cells may be seen.
 multi nucleated giant cells
multi nucleated giant cells
-Areas of aneosinophilic materials may be present that is considered by some authors to represent dysplastic dentin [dentinoid] as a result of inductive effect by odontogenic epithelium into mesenchymal tissues.
-About 20% of these cysts seen with the conjucation of odontomas.
-Some ameloblastomas have ghost cell differentiations giving rise to the concept that calcifying odontogenic cyst may be associated with ameloblastoma ,still Query?
 The solid variant
The solid variant
Treatment,
Enucleation.
Sum up:
Calcifying odontogenic cyst or Gorlin cyst is a developmental cyst develops in bone between 2 teeth or may in soft tissue and has 2 solid variants: odontogenic ghost cell tumor and odontogenic ghost cell carcinoma .
N.B: Calcifying epithelioma of malherbe is a cutaneous counterpart of calcifying odontogenic cyst.